Abundance: common
What: flower buds, fruit
How: dry, boil, or roast flower buds then use like okra; fruit eaten raw or used like other berries
Where: West Texas desert areas, sunny, hillsides
When: flower buds in spring, fruit in fall & winter
Nutritional Value: unknown
Dangers: spines and glochids must be removed before eating. Large amounts of flower buds can cause diarrhea
Medicinal Summary:
Fruit - diuretic, soothes urinary tract pain/irritation (raw, tisane)
Sap - soothes gastrointestinal inflammations; anti-diarrheal, soothes skin irritations (poultice)
Flower Buds - laxative
Root - prevents kidney stones (tisane)
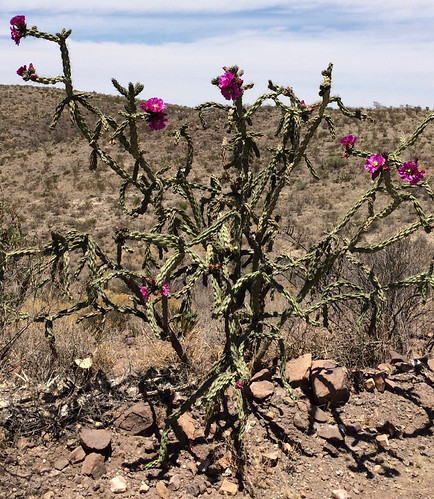
Tree cholla cactus, also known as cane cholla in Big Bend Ranch State Park, April 2018

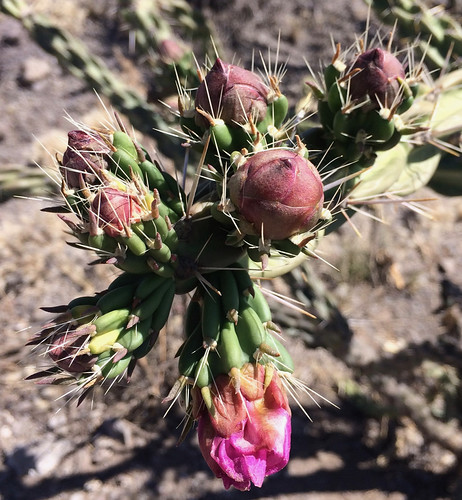
Tree cholla flower buds.


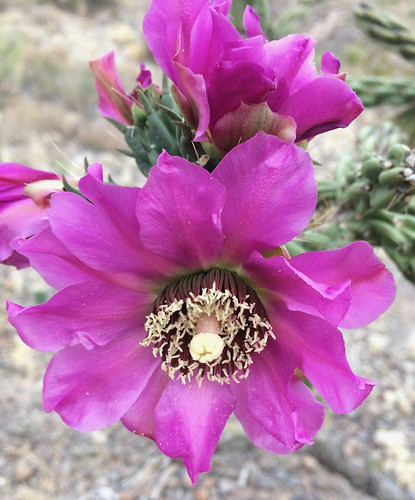
Opened flowers of tree cholla.
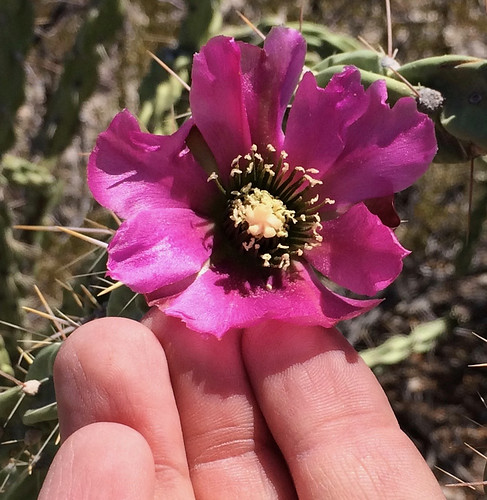


Unripe tree cholla fruit (they need to be more yellow).

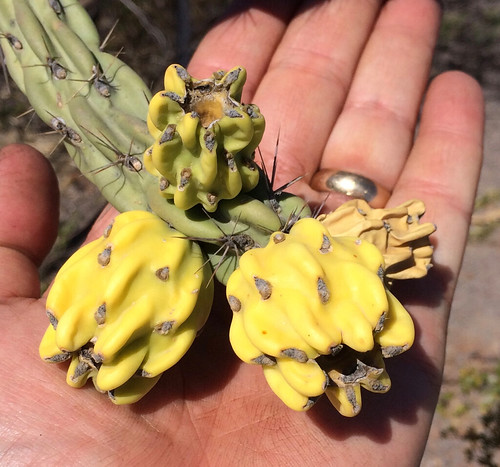
Overly ripe fruit (found in the spring rather than fall/winter).

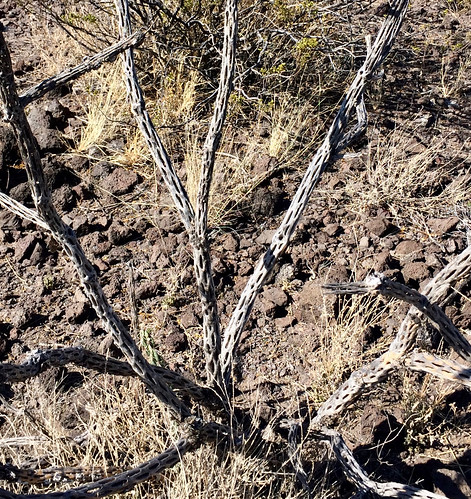
Dead tree chollas look kind of cool and are surprisingly strong.

Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
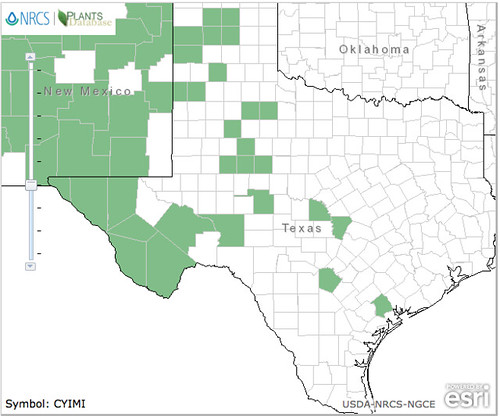
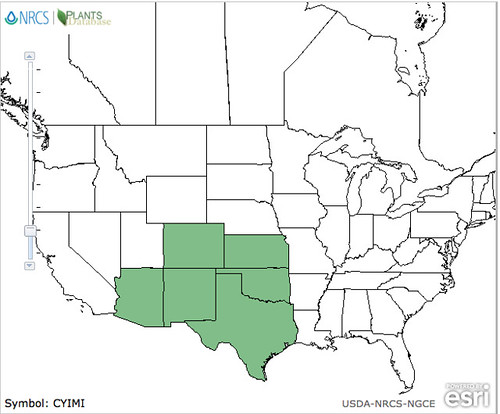
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
The many-trunked limbs, each about 1.5" in diameter and covered in many ~0.5" spines, of tree cholla dot the hillsides of the southwestern Texas Chihuahuan desert. These common cacti can grow to eight feet tall and in the spring there purple flowers stand out strongly from the reddish-brown desert. In the fall the branch tips will be covered in fleshy, yellow fruit, again about 1.5" in diameter and approximately 1.5" long. Dead tree chollas lose their skin and soft tissue to reveal an odd skeleton of wood perforated with a pattern of oblong, narrow holes. These dead branches are surprisingly tough and are used to make walking sticks.
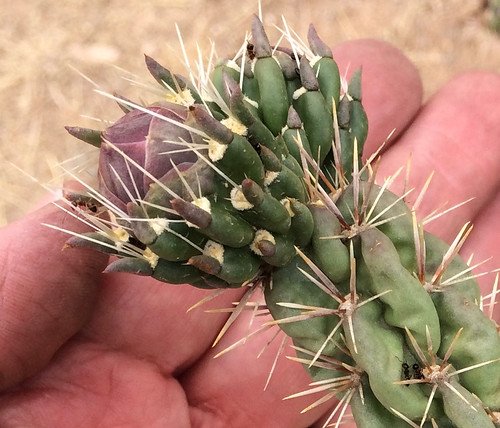
In the spring the flower buds can be harvested for food but beware the many spines, both large and small, that protect these buds. Tongs and a sharp, long-bladed knife are the best tools for collecting them. Burn off the spines with a propane torch or rub them gently but thoroughly with gravel to break the spines of the buds. Once these spines are removed the flower buds can be dried/dehydrated for later use. Natives of the desert would grind the dried flower buds into a flour-like powder. If you want to use the buds right away I'm told they should be boiled first for a bit to tenderize them some, then use them like okra or Brussel sprouts.
Come fall, the ripe fruit can be collected with the same tongs and knife, followed by removal of the spines. These juicy, yellow fruit have a sour flavor with a salty side. Once the spines are removed they can be eaten raw. Another favorite way to prepare them is in a fruit smoothie. Their salt content can help people in the early stages of dehydration (assuming water is available) by replenishing salts lost to sweating. I'm think slices of the fruit would work as a pickle-substitute on a hamburger but I haven't had a chance to try that yet.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.

