Abundance: common
What: sap
How: boiled down to give a syrup
Where: sunny edges of woods, along banks of rivers and lakes
When: sap flows best in winter just before leaf buds appear
Nutritional Value: calories, water

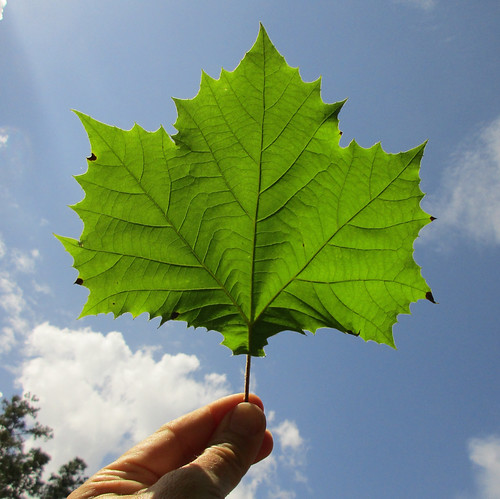
Sycamore leaves are similar in shape to their relative, the maple.

Mature sycamore leaves are huge, easily reaching more than 12" across.

In the winter the deciduous sycamores lose their leaves leaving behind inedible seed pods.

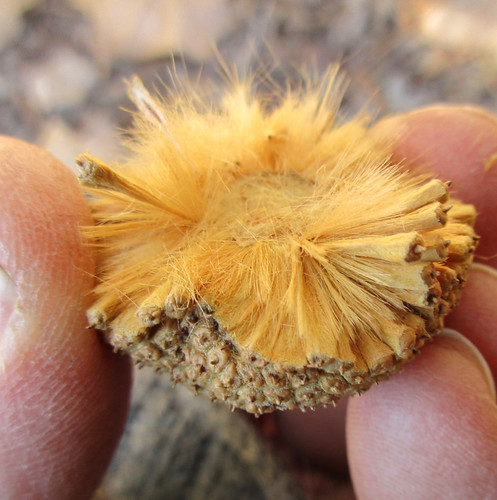
Close-up of seedpod and its many achenes.

Seep pod split open to reveal fuzzy interior.

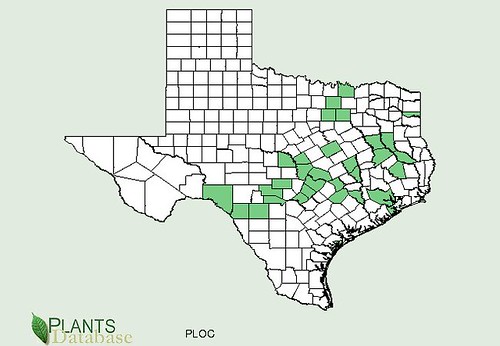
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.

The sycamore is a relative of maples and so can be tapped in late winter for sap. Sycamore syrup is much lower quality than maple syrup and takes approximately 50 gallons of sap to produce 1 quart of syrup. Generally this not considered to be worth the effort. However, this sap flows strongly and can be used as an emergency source of water throughout most of the year.
While inedible, the fruit which consists of a cluster of many seeds, is still useful. Left intact, the fruit make a somewhat durable bobber for fishing, though if the water does penetrate the fruit it'll eventually sink. The fluff inside the fruit can be used as tinder to start a fire.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.

