Abundance: plentiful
What: young leaves, flowers
How: tea and small addition to salads, sautéed
Where: fields, borders
When: late summer, early fall
Nutritional Value: low
Medicinal Summary:
Leaves/Flowers - vascular strengthener; anti-inflammatory; diuretic; anti-spasmodic; antibacterial; antifungal; hemostatic, rebuilds vascular/fluid-holding tissues (tisane, tincture, poultice)
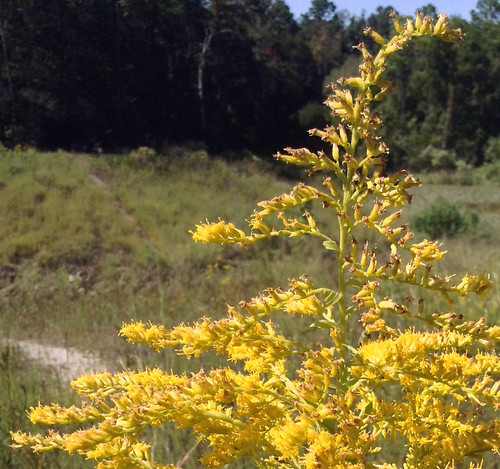
Goldenrod in the fall.

Close-up of goldenrod flowers.

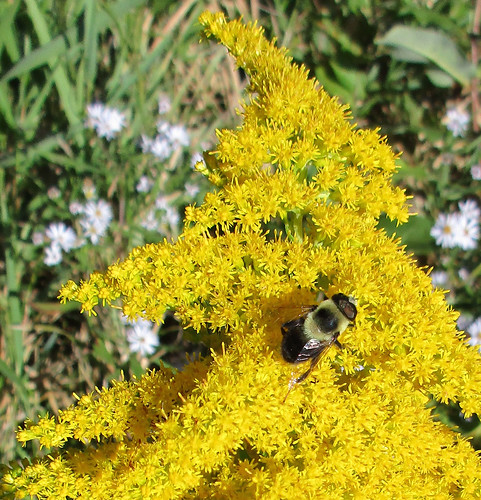
Goldenrod flowers are usually bees last source of nectar before winter hits.

Goldenrod seedlings appear in mid-winter to early spring.

The easiest way to recognize them when young is finding them where last year's brown, dry goldenrod stems stand, such as in this photo.

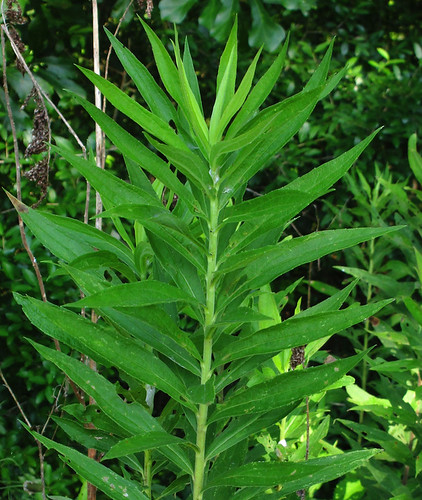
Young goldenrod plant (with more in the background) in late spring. These the young leaves make a tasty tea.

Close-up of goldenrod leaves. Note also, the stem is relatively smooth and hairless.


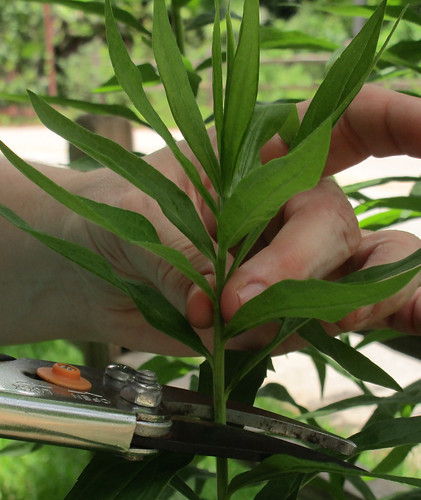
To properly harvest goldenrod leaves snip just the last 3"-4" where the leaves are lighter green.

By mid-summer many goldenrods have developed these round "galls" in their stems. Each gall is the home of a single, small grub of the Goldenrod Gall Fly. Note, these grubs are edible and also make good fishing bait.

Flowers before they bloom.

Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.

North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
Goldenrod can be found lining the roads and standing in fields in every US state and Canadian province. Most of the year they go unnoticed, their green stem and leaves acting like camouflage against the background of green grasses. Come fall, they explode like golden fireworks of deep yellow, pyramidal-clustered flowers. At this time they often get blamed wrongly for hay fever and allergy problems when in reality Ragweed, with it's almost invisible flowers, that is actually to blame.
The youngest, most tender leaves, when used in moderation, add an interesting dimension to the flavor of salads. There is often a noticeable color difference between the top 1"-3" of the stem (lighter) and lower parts (darker). Cut the goldenrod off at the point where the light color turns darker. These top leaves are the best for both raw snacks and dried tea.
The leaves can be collected and dried for tea any time from seedling until the flowers bloom. Once the flowers bloom the leaves begin deteriorating and usually are no longer worth collecting. For a black licorice-flavored tea, cut the young leaves or flower stalks off the plant in late morning after dew has evaporated but before the hot sun bakes them. Gather the flowers within the first few days of them opening for the richest flavors. Hang the flower stalks upside-down to dry inside a brown paper bag to dry. Steep one teaspoon of the dried flowers in hot water to make an anise-flavored tea.
Please note though that Goldenrod is the last flower of the season for bees to collect nectar. If you take many of the flowers you may prevent a bee hive from getting enough nectar to get through the winter. This is why I only take leaves.
Many goldenrods will form round galls on their stems. These are caused by a fly grub which is also edible by humans though most prefer to use the grub as fishing bait.
While dried goldenrod leaves can be smoked as an herbal tobacco replacement, it is generally used medicinally in tea form. A goldenrod infusion is diuretic and so good for flushing out urinary tract infections and kidney stones but I prefer its antioxidant properties and assistance in circulation by strengthening capillary walls. Goldenrod also assists with respiratory and sinus issues as well as loosening phlegm. Don't forget to infuse some oil with goldenrod then thicken it with beeswax as a skin salve. It can help induce sweating to expel toxins via the skin and its slight astringency makes its tea a good body wash for cleaning and tightening skin.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.

